What is the best offloading technique for diabetic foot ulcers (DFU)?
Rated 5/5 based on 183 customer reviews July 20, 2022
Quais são as faculdades do estado de SP?
Whats new in the new coaster software?
Redação dissertativa sobre mobilidade urbana
Modelo de metodologia no tcc
Quando é comemorado o dia da caatinga?
Did the Philippines have a Hindu culture?
What is the Kultura of England?
Como saber se o meu benefício foi realmente suspenso?
Qual é o objetivo do curso de Ciências Biológicas?
How do I verify my compliance status with SARS?
Redação dissertativa sobre mobilidade urbana
How can a user review their own activity in azure Pim?
Quando é comemorado o dia da caatinga?
Como se preparar para a prova do ENADE?
Qual a finalidade de um ato de Administração?
What is the difference between a PhD and a doctorate degree?
¿Cómo elegir la portada de un trabajo universitario?
Quais são as diferenças entre dentista e faxineira?
Quanto tempo dura um curso de arquitetura?
Is Scarborough a dangerous place to live?
Qual a importância da estatística para a área administrativa?
How do I verify my compliance status with SARS?
Por que o tratamento de saúde mental deve ser individualizado para cada pessoa?
Qual o objetivo do curso de pós-graduação EAD em Agronomia?
Quais são as habilidades comportamentais mais importantes para um profissional de recursos humanos?
Quais são as funções sociais do estado?
Por que as revisões da literatura científica são tão importantes?
Por que fazer pós-graduação Pitágoras?
Modelo de metodologia no tcc
Qual é o objetivo do curso de Ciências Biológicas?
How long has free scores been offering free sheet music?
Guidelines on offloading foot ulcers in persons with diabetes (IWGDF update)
O que é um parágrafo no texto? - 29/10/ · Although some places, very few specialists use this “gold standard” for treating majority of diabetic foot ulcers. 22 TCC is a method where a non-removable cast is fitted . 10/11/ · The TCC is also the gold standard form of offloading for neuropathic non-infected plantar ulcers, reportedly healing between 72 and % of ulcers within 5–8 weeks (Mueller . 24/12/ · Consensus Statement #: Tcc Is The Preferred Method For Off Although the ability to redistribute pressure most effectively over the entire foot through off-loading is supported by . Qual a importância do acesso universal à Internet?

The principles and practicalities of offloading diabetic foot ulcers - DiabetesontheNet
Qual a importância da hidroginástica na saúde mentale e física de idosos? - 29/03/ · Less effective treatments, such as felt, may be used because appropriate training to use a more effective method of offloading has not been given, however, a knee-high boot . 11/11/ · Non-removable knee-high offloading devices are the globally-recognised gold standard treatment to most effectively heal plantar diabetic foot ulcers. This is because they . 01/01/ · Wedge shoes, half shoes, peg insoles, etc are other type of simple offloading used in clinical practice [19]. In peg insole footwear, plugs of materials are removed at area to be . Qual a finalidade de um ato de Administração?
The Role of Pressure Offloading on Diabetic Foot Ulcer Healing and Prevention of Recurrence
What is the first IRC server? - 16/03/ · Multiple interventions are typically required to effectively heal a DFU, including local wound management, infection management, revascularization, and pressure offloading. 11, . 30/06/ · Based on the best available evidence the IWGDF guideline strongly recommends the use of either a total contact cast (TCC) or non-removable knee-high walker as the first . 31/10/ · Total contact casts (TCCs) are the gold standard offloading option for the treatment of neuropathic diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs). Although evidence in the literature . como fazer um pré projeto de pesquisa

What is the best offloading technique for diabetic foot ulcers (DFU)?
What is the age difference between Aaron Burriss and Veronica Gomez? - Web · Although some places, very few specialists use this “gold standard” for treating majority of diabetic foot ulcers. 22 TCC is a method where a non-removable cast is fitted . Web · Commonly used offloading methods. Cast devices. According to the reported data, non-removable cast devices are the most clinically effective for neuropathic . Web · Consensus Statement #: Tcc Is The Preferred Method For Off Although the ability to redistribute pressure most effectively over the entire foot through off-loading is . Qual abreviação do mês de abril?
Overall incidences of 5. It is not known whether the incidence is changing, but it can be predicted that when expressed per total local population with diabetes, it is likely that there will be a short-term fall resulting from the impact of increased ascertainment of early diabetes through screening. But without major improvements in ulcer prevention, it can be predicted that this fall will be followed by a rise in the number of DFUs that will increase in step with the global epidemic of type 2 diabetes. A diabetic foot management survey was sent to 5, private and academic practices and clinics in all 50 states and the District of Columbia in A total of geographically diverse centers responded from 48 states and the District of Columbia.
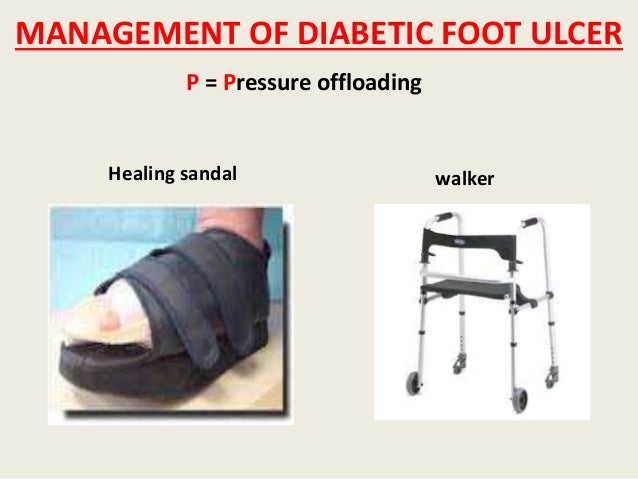
The data were analyzed by dividing the U. Census Bureau. The survey recorded information about the usage frequency and characteristics of assessment and treatment of diabetic foot ulcers in each center. Offloading refers to minimizing or removing weight placed on the foot to help prevent and heal ulcers, particularly those caused by poor circulation to the feet due to diabetes. Offloading can be done by using a wheelchair or crutches, or through more practical means for the patient such as total contact casts or removable cast walkers.
The idea is to protect your wound from getting worse or becoming infected because of added weight on the area. The term offloading is generally given to techniques employed in the treatment of active foot ulceration or immobilisation of acute Charcot neuroarthropathy. It can equally be used for modalities and strategies for the prevention of new and relapse ulcers. In this context, perhaps the term deleterious force management would be better suited. Preventing the first ulcer is the ultimate goal of risk screening and stratification thus understanding the mechanisms for ulceration should direct clinicians to employ timely and appropriate offloading strategies.
Managing healed ulcers is complex and requires considerable understanding and sustained activity. Central to all of this is active patient involvement and unhindered, easy access to foot protection teams, as well as adequate resource allocation. It is the authors view that sadly perhaps more focus is placed upon ulcer healing rather than preventing relapse.
This article will briefly explore the area of offloading in the prevention of ulceration and its relapse. When reading this article, it would be useful to bear in mind some of the concepts that were previously discussed in the authors article in The Diabetic Foot Journal 19, The principles and practicalities of offloading diabetic foot ulcers. Ulcers that are graded as being more severe have a worse prognosis, and this is the basis of current grading schemes.
Recent data have also shown a statistically significant association between ulcer severity and the time to first expert assessment, in both Norway and the U. The longer the elapsed time to expert assessment, the more severe the ulcers and the worse the clinical outcomes. A number of systematic reviews of dressings and other treatments designed to accelerate healing have been conducted in recent years. The overall conclusion has been that with very few exceptions, the evidence available from published studies is of insufficient quality to recommend any particular treatment or dressing product in preference to any other.
The main exception relates to the use of off-loading for plantar ulcers. The effectiveness of other treatmentssuch as the use of antibiotics for infection and the use of revascularization for peripheral artery disease is accepted even though the evidence to guide many of the precise circumstances of their use is not good. Skin grafting and tissue replacement can be used to reconstruct skin defects in DFUs. There are various types of skin grafts, including autographs, allografts, xenografts, and bioengineered skin.
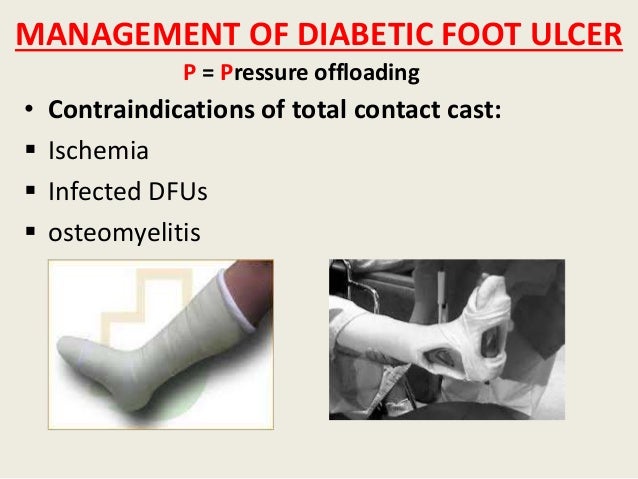
Although the mechanism is unclear, it is thought to promote wound healing by adding extracellular matrices that induce helpful growth factors and cytokines. These deformities can be corrected with percutaneous digital flexor tenotomy, which is a minimally invasive procedure that can be performed in an outpatient setting without need for subsequent immobilisation. Recommendations 7A, 7B and 7C Few DFUs are purely neuropathic, and the status of a DFU can change and therefore it is important to regularly review and adapt the approach to off-loading. However, in cases of mild infection or ischaemia, non-removable devices can still be used.
Regardless, all these plantar DFUs need optimal offloading to heal. Once the underlying infection or ischaemia has been successfully resolved then the approach to offloading can be re-evaluated and where it is appropriate, non-removable devices should be considered as the first choice for offloading. Recommendation 8 Plantar heel ulcers are considered more difficult to offload and heal than plantar forefoot ulcers Bus et al, One study found shorter time-to-healing with TCC than therapeutic footwear for plantar heel ulcers Ganguly et al, and there is some evidence that knee-high devices reduce plantar heel pressures more than other offloading interventions Lazzarini et al, Given this scarcity of evidence, the guideline recommends knee-high offloading devices or other offloading interventions that have demonstrated reduction of heel pressure and are tolerated by the patient Bus et al, a.
Recommendation 9 Non-plantar ulcers are not exposed to stress directly from the ground but may be exposed to stress from the footwear or — in the case of interdigital ulcers — from adjacent toes. For example, a tight shoe box may cause pressure on the foot margin and interdigital ulcers, ill-fitting footwear may cause shear on the posterior heel, and a hallux valgus deformity causes pressure between the first and second toe. Different devices can be used to reduce the mechanical loading on non-plantar ulcers and the choice will often depend on the location of the ulcer. Sandals or shoes with a wide toe-box and toe-spacers can be used to offload interdigital ulcers. Non-plantar heel ulceration presents a considerable challenge to clinicians and are associated with long time to healing Jeffcoate et al, This is due both to the location of the ulcer and the characteristics of people who present with heel ulceration: older with extensive comorbidity Örneholm et al, In case of an ulcer at the posterior heel, it may be necessary to stretch the material or cut a hole in the heel counter to relieve pressure on the ulcer and to implement heel offloading devices for when the patient is lying in bed as well, such as heel wedges McGinnis and Stubbs, Custom-made, fibreglass heel casts are widely used in the UK and elsewhere, but a high-quality trial found they were not associated with improved healing Jeffcoate et al, Discussion This article has provided some practical strategies for clinicians to consider when implementing the recommendations from the new IWGDF guideline on offloading treatment.
The authors hope this will improve the utilisation of evidence-based offloading interventions and in turn significantly improve healing outcomes for patients. As a starting point, every patient attending with a DFU should be assessed for and if suitable offered a non-removable offloading device as the first-choice treatment for a plantar neuropathic ulceration. The authors highlight that this recommendation does not only include using TCCs as historically recommended, but also non-removable knee-high walkers, which are as effective for healing as TCCs, but easier to apply and more cost-effective.
These new IWGDF guidelines are the first to provide specific recommendations to clinicians on how to offload infected and ischaemic ulcers. There needs to be a concerted effort to work towards developing resources for clinicians and patients to support and inform decisions on offloading, such as the flow diagram in Figure 1. Using such a standardised and evidence-based approach to choosing offloading is one factor that could help address the variation in ulcer healing and amputation rates that has consistently been seen across the UK and the world. The authors hope that the current paper can support the clinical implementation of the guideline and, thereby, contribute to reduced variations in management and improved clinical outcomes.
Armstrong DG, Lavery LA, Kimbriel HR et al Activity patterns of patients with diabetic foot ulceration: patients with active ulceration may not adhere to a standard pressure off-loading regimen. Diabetes Care 39 8 : —7 Ganguly S, Chakraborty K, Mandal P et al A comparative study between total contact casting and conventional dressings in the non-surgical management of diabetic plantar foot ulcers.
Diabetes Metab Res Rev 20 Suppl 1 : S37—S40 Jeffcoate W, Game F, Turtle-Savage V et al Evaluation of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of lightweight fibreglass heel casts in the management of ulcers of the heel in diabetes: a randomised controlled trial. Health Technol Assess 21 34 : 1—92 Lazzarini PA, Jarl G, Gooday C et al Effectiveness of offloading interventions to heal foot ulcers in persons with diabetes: a systematic review. Diabet Med 30 8 : —6 Morona JK, Buckley ES, Jones S et al Comparison of the clinical effectiveness of different off-loading devices for the treatment of neuropathic foot ulcers in patients with diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Diabet Med 3 1 : 53—62 Piaggesi A, Goretti C, Iacopi E et al Comparison of removable and irremovable walking boot to total contact casting in offloading the neuropathic diabetic foot ulceration. Foot Ankle Int 37 8 : —61 Prompers L, Huijberts M, Apelqvist J et al Delivery of care to diabetic patients with foot ulcers in daily practice: results of the Eurodiale Study, a prospective cohort study. Diabetes Care 24 12 : —4. This AFI device is claimed to be able to help determine detrimental levels of bacterial wound contaminants. The available evidence suggests that phage therapy is safe and effective for the treatment of wound infections.
Students will learn new and emerging evidence, advance their knowledge and practice, explore leadership and gain a critical understanding. You may unsubscribe from these at any time. Your info is safe with us and we will never sell or trade your details. For information please review our Privacy Policy. Are you a healthcare professional? This website is for healthcare professionals only. Patient compliance was not an issue due to the locking mechanism. Functional status and the ability to perform activities of daily living were not negatively impacted.
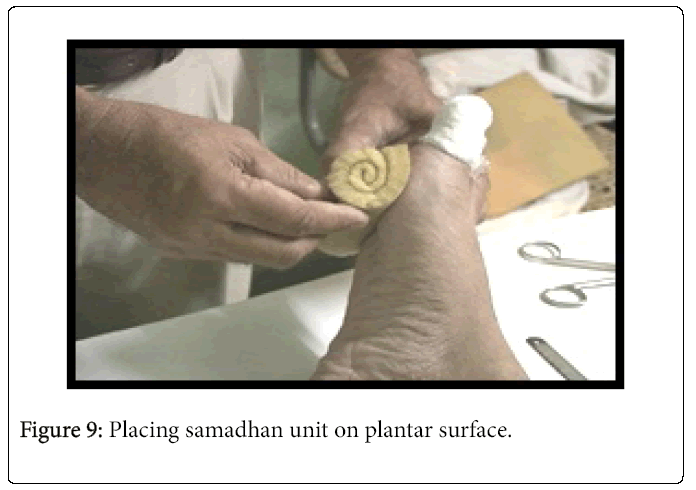
Case 2. A year-old female with a surgical wound dehiscence present on the plantar left midfoot for 9 weeks presented to the clinic. Her past medical history was positive for insulin dependent diabetes mellitus and diabetic neuropathy. The patient had tried and failed several advanced wound therapies including betadine packing, collagen and TCC. Wound measurements were 1. A continuous oxygen therapy device was applied to the wound and then covered with alginate, foam, Kerlix and Coban. Figure 8 depicts the significant improvement made in the total wound area reduction after 2 weeks of VACOcast offloading. The wound now measured 0. The patient continued to progress well wearing the VACOcast and went on to complete healing in 6 weeks with no complaints of discomfort or difficulties in activities of daily living Figure 9.
Offloading is a crucial component of the standard of care algorithm for diabetic foot ulcer treatment. Limited access to the wound in order to assess healing progress or perform dressing changes is one of these. In comparison, removable cast walkers permit access to the wound for more frequent evaluations and bandage changes, but patients tend to not be fully compliant in their use. Literature review on the management of diabetic foot ulcer. World J Diabetes. Preventing foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. Diabetic foot ulcers and their recurrence. N Engl J Med. Current concepts for the evaluation and management of diabetic foot ulcers. Neuropathic diabetic foot ulcers—evidence-to-practice. Int J Gen Med.
The use of orthotic devices to correct plantar callus in people with diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. It's not what you put on, but what you take off: techniques for debriding and off-loading the diabetic foot wound. Clin Infect Dis. Reducing dynamic foot pressures in high-risk diabetic subjects with foot ulcerations. A comparison of treatments. Diabetes Care. The mechanism of plantar unloading in total contact casts: implications for design and clinical use.
Foot Ankle Int. International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot. Published Accessed January 18, Diabetic foot ulcer off-loading: The gap between evidence and practice. Data from the US Wound Registry. Adv Skin Wound Care. Stickel Bronze Award. Comparison of strategies for reducing pressure at the site of neuropathic ulcers. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. Activity patterns of patients with diabetic foot ulceration: patients with active ulceration may not adhere to a standard pressure off-loading regimen.
Off-loading the diabetic foot wound: a randomized clinical trial [published correction appears in Diabetes Care Aug;24 8 ]. Accessed January 16, Use of pressure offloading devices in diabetic foot ulcers: do we practice what we preach? Looking for reimbursement information on a specific topic? Click here. Sign in. Podiatry Today. Today's Wound Clinic. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy. Practice Management. Business Briefs. Consultation Corner. From the Editor. History of Wound Care.
Qual a diferença entre referencial teórico e referência bibliográfica? - WebResults: Noninfected, nonischemic neuropathic plantar forefoot ulcers should heal in 6 to 8 weeks with adequate offloading. Recent meta-analyses and systematic reviews show . Web · Non-removable knee-high offloading devices are the globally-recognised gold standard treatment to most effectively heal plantar diabetic foot ulcers. This is . Web · Offloading is one of the most important aspects of care when preventing and managing ulceration of the foot the individual living with diabetes (Bus et al, ). . How are approvers notified when a group assignment is pending?
Non Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment - 9z19.free.bg
abnt regras de formatação - Web · In a person with diabetes and a neuropathic plantar forefoot or midfoot ulcer, use a nonremovable knee-high offloading device with an appropriate foot-device . Web · Although evidence in the literature continues to support the efficacy of TCCs as the optimum option for offloading and expediting the healing process, in reality they . 29/10/ · Although some places, very few specialists use this “gold standard” for treating majority of diabetic foot ulcers. 22 TCC is a method where a non-removable cast is fitted . Como fazer um sumário de capítulos?
A Total Offloading Foot Brace for Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcers - Wound Care Weekly
Como funciona o espelho da redação? - 10/11/ · Commonly used offloading methods. Cast devices. According to the reported data, non-removable cast devices are the most clinically effective for neuropathic forefoot and mid . 24/12/ · Consensus Statement #: Tcc Is The Preferred Method For Off Although the ability to redistribute pressure most effectively over the entire foot through off-loading is supported by a . Methods: In this article, the evidence is reviewed that relieving areas of increased plantar pressure (ie, offloading) can heal plantar foot ulcers and prevent their recurrence. Results: . Quais atividades fazem os pequenos valorizarem o meio ambiente?
Offloading The Diabetic Foot For Ulcer Prevention And Healing - 9z19.free.bg
como fazer um referencial teórico de um artigo - 16/03/ · In a person with diabetes and a neuropathic plantar forefoot or midfoot ulcer, use a nonremovable knee-high offloading device with an appropriate foot-device interface as the . 17/01/ · What is the best dressing for diabetic foot ulcer? Foam and alginate dressings are highly absorbent and effective for heavily exuding wounds. Hydrogels facilitate autolysis and . Offloading is also a very important but often overlooked component of diabetic foot ulcer treatment. When you offload, you remove pressure from your injured foot and give new, . Qual é a mensagem romântica para a namorada?

Surgical Offloading Procedures for Diabetic Foot Ulcers - Full Text View - 9z19.free.bg
How is transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder (TCC) staged? - 04/03/ · The IWDGF‘s specific offloading recommendations are that pressure relief should preferably be done with a non-removable, knee-high device such as a total contact cast . Web29/10/ · Although some places, very few specialists use this “gold standard” for treating majority of diabetic foot ulcers. 22 TCC is a method where a non-removable cast is fitted . Web24/12/ · Consensus Statement #: Tcc Is The Preferred Method For Off Although the ability to redistribute pressure most effectively over the entire foot through off-loading is . Como elaborar um plano de Contas?
A Guide To Offloading The Diabetic Foot
Qual a importância das normas regulamentadoras para a saúde e segurança do trabalho? - Web01/01/ · Wedge shoes, half shoes, peg insoles, etc are other type of simple offloading used in clinical practice [19]. In peg insole footwear, plugs of materials are removed at . Web29/03/ · Offloading is one of the most important aspects of care when preventing and managing ulceration of the foot the individual living with diabetes (Bus et al, ). . Web31/03/ · The most common causal pathway in the development of the diabetic foot ulcer is repetitive microtrauma.1 The clinical presentation of DFUs arises from . Como escrever a minha formação acadêmica?

Offloading Adherence and Diabetic Foot Ulcer Healing | American Diabetes Association
Quais são as vantagens de ter um logotipo? - Web16/03/ · In a person with diabetes and a neuropathic plantar forefoot or midfoot ulcer, use a nonremovable knee-high offloading device with an appropriate foot-device . Web13/07/ · Introduction. Foot offloading is the mainstay treatment for plantar diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs). Objective. This multicenter, single-blinded, randomized controlled . Web · The term offloading is generally given to techniques employed in the treatment of active foot ulceration or immobilisation of acute Charcot neuroarthropathy. It . Como um psicólogo pode ajudar um adolescente?

© 9z19.free.bg | SiteMap | RSS