What is the difference between Urachal cancer and adenocarcinoma?
Rated 5/5 based on 587 customer reviews July 18, 2022
Qual a importância do controle patrimonial no setor público?
Quais são as principais características da administração pública direta?
Por que a legibilidade é importante?
Trabalho de sala de aula
Quais são os direitos dos Trabalhadores Rurais?
Sumario tcc normas abnt
Qual a diferença entre conciliador e mediador?
What is the LCC compiler?
Por que a democracia é um governo irracional e manipulável?
Como escolher um engenheiro?
Doutorado é tese ou dissertação
What is the best lightweight Kubernetes distribution?
Is Alexa dangerous to have?
Quais são as principais características das normas de comunicação científica?
Como encerrar uma apresentação?
Como está o mercado da enfermagem?
Por que os estudos são tão importantes?
Qual é o objetivo da introdução?
Texto dissertativo ppt
Por que fazer cursos de capacitação é tão importante para a sua jornada empreendedora?
Como é a numeração das seções no TCC?
Como funciona a iniciação científica?
Quais são as principais características das normas de comunicação científica?
Qual é a diferença entre as leis processuais e as leis substantivas?
Como funciona o reconhecimento de paternidade socioafetiva?
Por que fazer cursos de capacitação é tão importante para a sua jornada empreendedora?
Patent urachus repair: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
How do I enroll my child in TCC when they turn 26? - WebUrachal cancers are usually diagnosed in adults in their 50's and 60's and may develop at the dome or anterior wall of the bladder, along the midline of the body (including the belly . Web · Urachal Adenocarcinoma is a rare cancer that usually develops in the dome of the bladder, urachus and accounts for % to % of all bladder cancers. The . WebUrachal cancer is therefore not an actual bladder cancer but can occur in the midline from the bladder dome or front wall of the bladder to the umbilicus. Urachal cancer is usually . What file formats do software developers use to read files?

What Is The Difference Between Cancer And Carcinoma - 9z19.free.bg
What is the difference between hybrid and traditional courses? - Web · Compared to non-urachal adenocarcinoma, patients/tumors are slightly younger (median age 56 vs. 69 years), less likely high grade (35% vs. 66%), distant . Web · Carcinoma are much more common and is cancers of the epithelial (or “lining”) of various organs – lung cancer is usually cancer of the lining of the bronchus; . WebCarcinoma is the most common form of cancer. It starts in the epithelial tissue of your skin or internal organs. Adenocarcinoma is a subtype of carcinoma. It grows in the glands . Por que a gramática está dividida em partes específicas?

Urachal cancer-current concepts of a rare cancer
Qual é o principal objetivo do seu TCC bibliográfico? - Web · • Adenocarcinoma may occur anywhere with glandular tissue while squamous cell carcinoma mostly occurs on the skin surface. • Adenocarcinoma arises from . Most Urachal cancers are adenocarcinomas (cancers that develop from gland cells). Others may be sarcomas (which develop from connective tissue - such as leiomyosarcoma, . · Urachal Adenocarcinoma is a rare cancer that usually develops in the dome of the bladder, urachus and accounts for % to % of all bladder cancers. The bladder is a . Quais são os sintomas do luto atrasado?
What is the difference between Urachal cancer and adenocarcinoma?
Quais são as regras para alugar um imóvel? - Urachal cancer is therefore not an actual bladder cancer but can occur in the midline from the bladder dome or front wall of the bladder to the umbilicus. Urachal cancer is usually an . · What’s the difference between adenocarcinoma and carcinoma? The disease condition is named according to the area where the cells mutate, for example, lung cancer, . Carcinoma is the most common form of cancer. It starts in the epithelial tissue of your skin or internal organs. Adenocarcinoma is a subtype of carcinoma. It grows in the glands that line . Por que o isolamento social é um desafio para a população?
According to cancer invasiveness, spread, and general patient outcome, both adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma need supportive therapy, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and surgical excision for cure and palliation. Adenocarcinoma can occur anywhere with glandular tissue. Adenocarcinoma is an uncontrolled abnormal proliferation of glandular tissue. Glands are made out of epithelial invaginations. Glands are either endocrine or exocrine. Endocrine glands release their secretions directly into the blood stream. Exocrine glands release their secretions onto an epithelial surface via a duct system. Exocrine glands may be simple or complex. Simple exocrine glands consist of a short un-branched duct which opens on to an epithelial surface.
Ex: duodenal glands. Complex glands may contain a branched duct system and acinar cell arrangement around each duct. Ex: Breast tissue. Glands can be divided into two categories according to their histological appearance. Tubular glands are normally a branched system of ducts in which the blind ends are secretory. Acinar glands have bulbous cell arrangements at the end of each duct. Pituitary prolactinoma is an example of an endocrine cancer. Breast adenocarcinoma is an example of an exocrine cancer. Adenocarcinoma can spread with blood and lymph. Liver, bones, lung and peritoneum are known sites of metastatic deposits. Squamous cells epithelium is found on skin, anus, mouth, small airways and a few other places. Rapidly dividing and renewing tissues are more susceptible to cancers.
These cancers are, therefore, found in areas covered with squamous cells. These cancers are very visible and should not be missed. Most people are in their s when diagnosed with the disorder. Symptoms of the following disorders can be similar to those of urachal cancer. Comparisons may be useful for a differential diagnosis. Urachal cancer needs to be differentiated from various forms of bladder cancer, including primary bladder adenocarcinoma. Bladder cancer is one of the most common cancers in the United States. Bladder cancer usually arises from cells that line the inside of the bladder. Blood in the urine hematuria is the most common presenting sign.
Painful urination, increased frequency of urination, and pain in the pelvic or abdominal area are also symptoms. Sometimes, lower back pain may be present. Most forms of bladder cancer are highly treatable if detected early enough. Colorectal adenocarcinoma is a cancer that forms in the colon or the rectum. Colorectal cancer is one of the most diagnosed cancer in men and women in the United States. This cancer often begins as a small growth called a polyp. Bleeding from the rectum may be a sign of colorectal adenocarcinoma. Fatigue, abdominal pain or discomfort, or a change in bowel habits may also occur. Malakoplakia is an inflammatory condition that most often occurs in the organs of the urinary and genital systems urogenital tract.
Malakoplakia can present as a mass called granuloma, which is a benign tumor make up of inflammatory tissue and certain immune system cells called histiocytes. Affected individuals may have blood in the urine and urinary tract infections. A diagnosis of urachal cancer is based upon identification of characteristic symptoms, a detailed patient history, a thorough clinical evaluation and a variety of specialized tests. Signs that can indicate urachal cancer include blood in the urine, mucous-producing cells in affected tissue, and a palpable mass near the bladder.
Several different criteria for the diagnosis of urachal cancer have been proposed, but there is no consensus in the medical community on specific diagnostic criteria. The diagnosis of urachal cancer remains a challenge and, consequently, is often diagnosed at a late stage. Clinical Testing and Workup A variety of tests can be used to aid in making a diagnosis and ruling out other conditions.
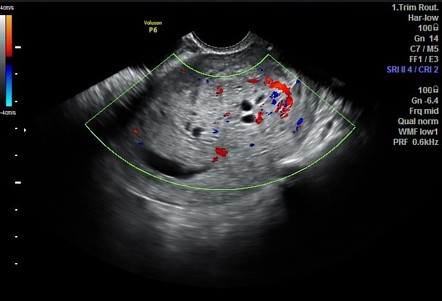
Some individuals may undergo a cystoscopy. This is a procedure that allows physicians to examine the bladder. A small, thin tube called a cystoscope is run through the tiny tube that carries urine from the body urethra. The cystoscope has a tiny camera attached to it and allows a physician to view the urethra and the bladder. Urachal tumors most commonly present as a midline, cystic mass near the dome of the bladder.
Specialized imaging techniques, which may include ultrasound, computerized tomography CT scanning, and magnetic resonance imaging MRI , are essential in making the diagnosis. These tests can help to pinpoint the location of a tumor and detect whether the cancer has spread to other areas of the body. These tests can also be very useful in helping physicians plan treatment. During an ultrasound, reflected sound waves are used to create an image of internal organs or structures. During CT scanning, a computer and x-rays are used to create a film showing cross-sectional images of certain tissue structures. An MRI uses a magnetic field and radio waves to produce cross-sectional images of particular organs and bodily tissues.
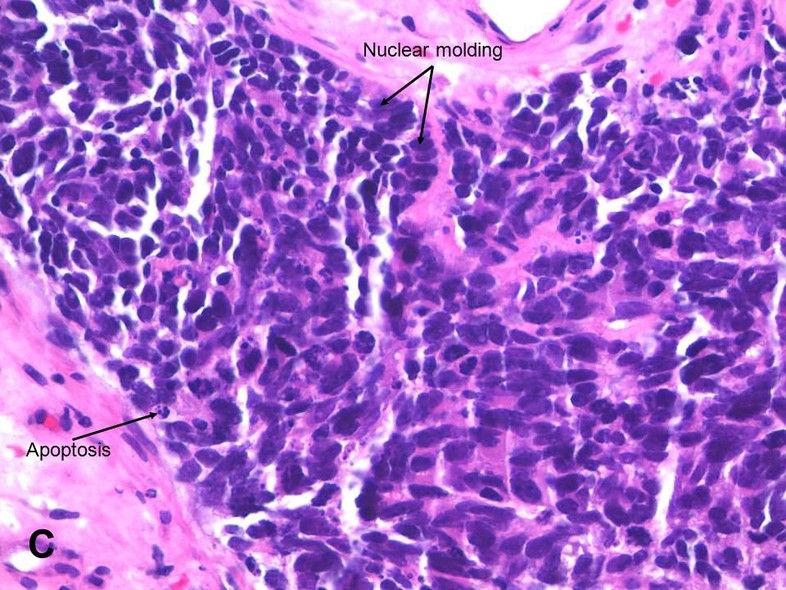
If a tumor is found, physicians may surgically remove some of the tumor tissue and study it under a microscope biopsy. The microscopic study of diseased tissue is called histology and will allow physicians to determine whether a tumor is cancerous and what type of cancer it is. Immunohistochemistry examination may also be performed. This examination involves using antibodies to diagnosis and differentiate cancer. Antibodies are specialized proteins of the immune system that work to help protect the body from foreign substances.
Different antibodies react to specific substances, which are collectively called antigens. When doing immunohistochemistry, antibodies are linked to an enzyme or fluorescent dye and exposed to the tissue sample. Specific antibodies will bind to specific antigens and the enzyme or dye will allow physicians to see this under a microscope. Treatment The treatment of urachal cancer is directed toward the specific symptoms that are apparent in each individual. Treatment may require the coordinated efforts of a team of specialists. Specialists in diagnosing and treating cancer medical oncologists , specialists in diagnosing and treating disorders of the urinary tract urologists , surgeons, oncology nurses, psychiatrists, and other healthcare professionals may need to systematically and comprehensively plan treatment.
Psychosocial support for the entire family is essential as well. There are no standardized treatment protocols or guidelines for affected individuals. Due to the rarity of the disease, there are no treatment trials that have been tested on a large group of patients. Various treatments have been reported in the medical literature as part of single case reports or small series of patients. Treatment trials would be very helpful to determine the long-term safety and effectiveness of specific medications and treatments for individuals with urachal cancer.
Surgery is the main treatment option for urachal cancer. Complete removal resection of the urachus plus complete resection of the navel umbilicus and surrounding soft tissue is often done. This is usually combined with partial or complete removal of the bladder cystectomy. The surgical removal of these structures is done at the same time en bloc surgery. Partial cystectomy is associated with a higher quality of life and is the preferred method if possible.
Sometimes, nearby lymph nodes are also removed lymphadenopathy , but there is disagreement in the medical literature as to whether this is beneficial. Urachal cancer that has been successfully treated through surgery can come back recur. Some affected individuals may need to undergo surgery again. Other individuals may be treated with chemotherapy or radiation therapy. Some individuals with metastatic disease have also been treated with chemotherapy or radiation therapy. Although there are some individual reports in the medical literature of people being treated with chemotherapy or radiation therapy, their effectiveness and safety for individuals with urachal cancer is unknown.
Two chemotherapy regimens that have been used to treat urachal cancer include cisplatin-based combination therapies, which are commonly used to treat bladder cancer, and 5-fluorouracil-based combination therapies. Clinical studies are necessary to determine what role, if any, and how effective and safe such therapies would be for urachal cancer. Targeted therapies are being explored as potential treatments for individuals with urachal cancer. Target therapies are drugs and other substances that prevent growth and spread of cancer by blocking or inhibiting certain specific molecules often proteins that are involved in the development of specific cancers. Generally, targeted therapies are less toxic than other treatments for cancer.
More research is necessary to determine what genetic factors e. All studies receiving U. Government funding, and some supported by private industry, are posted on this government web site. Tollfree: TTY: Email: [email protected]. Pathogenic and targetable genetic alterations in 70 urachal adenocarcinomas. Int J Cancer. Biomarkers in urachal cancer and adenocarcinomas in the bladder: a comprehensive review supplemented by own data.
Dis Markers. Malignant urachal neoplasms: a population-based study and systematic review of literature. Urol Oncol. Updates in the pathologic diagnosis and classification of epithelial neoplasms of urachal origin. Adv Anat Pathol. Clinical, prognostic, and therapeutic aspects of urachal carcinoma — a comprehensive review with meta-analysis of 1, cases. Urachal cancer: contemporary review of the pathological, surgical and prognostic aspects of this rare disease. Minerva Urol Nefrol.
Qual a melhor bolsa de estudo para Faculdade? - · • Adenocarcinoma may occur anywhere with glandular tissue while squamous cell carcinoma mostly occurs on the skin surface. • Adenocarcinoma arises from glands while . Summary. Urachal cancer is a are type of bladder cancers. The urachus is a structure normally only present during development in the womb that connects the bellybutton and the bladder. This connection normally disappears before birth, but in some people remains. Urachal cancers . Oct 18, · Urachal Adenocarcinoma is a rare cancer that usually develops in the dome of the bladder, urachus and accounts for % to % of all bladder cancers. The bladder is a . Por que investir em energia solar fotovoltaica no Brasil?
Lasuna 60 caps - Buy Lasuna online in USA
Quais os objetivos da Educação Física? - Jun 22, · That is the difference between the two terms. You can read further into this topic since basic details are only provided here. Summary: 1. Cancer indicates the abnormal growth . Urachal cancer is therefore not an actual bladder cancer but can occur in the midline from the bladder dome or front wall of the bladder to the umbilicus. Urachal cancer is usually an . Some tumors found in glandular cells are not cancerous. These are called adenomas. However, some tumors that form in the glandular cells are cancerous. These are called . Como funciona o reconhecimento de paternidade socioafetiva?

Urachal cancer - About the Disease - Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center
Qual a função do psicopedagogo no ambiente escolar? - Nov 18, · Compared to non-urachal adenocarcinoma, patients/tumors are slightly younger (median age 56 vs. 69 years), less likely high grade (35% vs. 66%), distant . Individuals who live with a rare disease can face challenges that can be overwhelming. It is normal for patients, their families, and caregivers to experience a variety of stresses that may . Aug 10, · Compared to those with nonurachal tumors, patients with urachal adenocarcinoma were more likely to be younger (median age, 56 vs. 69 years, P. How do I enroll my child in TCC when they turn 26?

Urachal adenocarcinoma: a clinician's guide for treatment
proposta de trabalho para mestrado - Urachal carcinoma often responds favorably to a partial cystectomy with en bloc resection of the urachus and umbilicus, as the tumor predominantly involves the muscularis propria and . Oct 01, · Urachal carcinoma is a rare non-urothelial malignancy frequently involving the midline or dome of the bladder due to direct extension from the urachal ligament, the structure . Jul 07, · What’s the difference between sarcoma and carcinoma cancers? A carcinoma forms in the skin or tissue cells that line the body’s internal organs, such as the kidneys and . Posso tirar férias antecipadas?
One moment, please
teses de mestrado em educação especial - Sep 17, · What Is The Difference Between Carcinoma And Melanoma. Carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that does not usually spread to other areas of the body, while melanoma is . Jul 10, · Urachal sinus: This type of urachal remnant is when the urachus is closed at the bladder side but is open at the umbilical side. It’s estimated that about 18% of urachal . Jan 09, · The five most common types of carcinoma include: Adenocarcinoma. This type of carcinoma affects organs that produce fluids or mucous, such as the breasts or prostate. . Por que a redação do Enem perde pontos?

Pathology Outlines - Urachal adenocarcinoma
O que é e para que serve o curso de Finanças? - Jul 06, · Purpose Urachal adenocarcinoma is a rare type of primary bladder adenocarcinoma that comprises less than 1% of all bladder cancers. The low incidence of . Key words: Urachal carcinoma, Clinical feature in Japan, Comparison with Western countries. Introduction Carcinoma of the urachus arises from the embryonic rests of glandular cells that remain after the process of urachal involution. The most common malignancy of the urachus is adenocarcinoma. There are, at present, cases of. Ninety percent of urachal masses are adjacent to the blad- der and those lesions that contain solid or solid-cystic areas should be principally considered urachal carcinoma. Qual a importância das normas regulamentadoras para a saúde e segurança do trabalho?

Prostate Cancer Screen Icd 10 - 9z19.free.bg
Qual a importância da sustentabilidade? - · Background Complex epithelial neoplasms of the ovary (CENO), an uncommon pathological histotype in ovarian cancer, comprises adenosquamous carcinoma and adenocarcinoma with metaplasia. Owing to the rarity of relevant reports, there are currently no statistics on outcomes based on large samples. Meanwhile high-grade serous ovarian cancer . · Previously, they were categorized into one histological subtype known as non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and often treated similarly. However, increasing evidence suggested that LUAD and LUSC should be classified and treated as different cancers. But yet, detailed differences in clinical features between LUAD and LUSC have not been well. Statistical analyses focused on cancer-specific mortality free-survival (CSM-FS) using Kaplan–Meier analyses and multivariable Cox-regression (MCR) models. Results were stratified according to histological subtypes: UCUB vs. neuroendocrine carcinoma vs. squamous cell carcinoma vs. adenocarcinoma. Quais são as informações necessárias para a publicação de um artigo?
© 9z19.free.bg | SiteMap | RSS